1. [4장 실습용 문제] (4-1에서 이어지는 문제)
/******************************************************************************
* 문제 4-2
******************************************************************************/
// 새로운 프로젝트와 Main.java 소스파일을 만든 후 [문제 4-1]에서 작성한 소스코드를 복사해서 삽입하라.
// [문제 4-2] 실행 결과를 참고하여 아래 코드를 작성하라.
// 1) 기존의 main() 함수 내에 있던 String[] name, int[] tall 변수를 Manager 클래스의
// static private 멤버로 옮겨라.
// 2) 아래 main() 함수에서 호출하는 Manager.makeManager(in) 문장을 참조하여 Manager 클래스에
// 해당 함수를 구현하라. 기존 [문제 4-1]의 main 함수에 있던 manager 객체
// 생성하는 코드들(while 문장 앞까지의 코드)를 makeManager(in) 함수로 옮기면 된다.
// 그리고 생성된 manager 객체를 리턴하면 된다.
// 3) Manager 객체는 항상 makeManager(in) 함수를 사용하여 생성하고 사용자가 직접
// new Manager(3) 형태로 호출하여 객체를 생성할 수 없게 하라.
// 4) 기존 main() 함수를 아래 main() 함수로 교체하라.
// 5) 메뉴 항목 "4.FindStudent2"를 선택할 경우 manager.findStudent(pname, tall)가 호출된다.
// 이 함수를 구현하라. 이 함수는 Manager가 관리하는 학생 중에 입력된 이름과 키가
// 각각 pname과 tall과 동일한 학생을 찾아 출력한다. 찾지 못한 경우 적절한 에러 메시지를 출력한다.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Manager manager = Manager.makeManager(in);
// manager = new Manager(3);
// 위 문장의 주석을 제거하면 Manager 생성자 접근할 수 없다는 에러가 발생하여야 한다.
while(true) {
System.out.print("\n0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean\n");
System.out.print("3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> ");
int input = in.nextInt();
if (input == 0)
break;
switch (input) {
case 1: manager.displayAll();
break;
case 2: manager.calculateMean();
break;
case 3: System.out.print("name? ");
String pname = in.next();
manager.findStudent(pname);
break;
case 4: System.out.print("name, tall? ");
pname = in.next();
int tall = in.nextInt();
manager.findStudent(pname, tall);
break;
case 5: manager = Manager.makeManager(in);
break;
}
}
in.close();
}
}실행결과 예시
===============================================================================
== [문제 4-2] 실행 결과
===============================================================================
input continuously 6 indices(index) of array: 0 1 2 3 4 5 // 사용자 입력: 0 ~ 5 숫자를 임의의 순서로 입력
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 1
name tall difference
bob 172 0.00
john 183 0.00
alice 168 0.00
nana 161 0.00
tom 171 0.00
sandy 172 0.00
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 2
tall mean: 171.17
name tall difference
bob 172 0.83
john 183 11.83
alice 168 -3.17
nana 161 -10.17
tom 171 -0.17
sandy 172 0.83
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 5
input continuously 6 indices(index) of array: 5 4 3 2 1 0 // 사용자 입력: 0 ~ 5 숫자를 임의의 순서로 입력
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 1 // 새로운 manager 객체가 생성되었고, 배열에 들어간 객체 순서도 다름
name tall difference
sandy 172 0.00
tom 171 0.00
nana 161 0.00
alice 168 0.00
john 183 0.00
bob 172 0.00
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 2
tall mean: 171.17
name tall difference
sandy 172 0.83
tom 171 -0.17
nana 161 -10.17
alice 168 -3.17
john 183 11.83
bob 172 0.83
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 4
name, tall? nana 161
nana 161 -10.17
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 4
name, tall? nana 160
nana 160: not found.
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 4
name, tall? NANA 161
NANA 161: not found.
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 4
name, tall? bob 171
bob 171: not found.
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 4
name, tall? bob 172
bob 172 0.83
0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean
3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> 0
2. 정답코드
import java.util.Scanner;
class Student {
// 아래 name, tall, diff는 반드시 private로 하라.
private String name;
private int tall;
private double diff;
public Student(String name, int tall){
this.name = name;
this.tall = tall;
}
public void printStudent() {
System.out.printf("%s\t%d\t%6.2f\n", name, tall, diff);
}
// 필요한 경우 멤버 값을 설정하고 구해오는 메소드(함수)를 만들어 멤버에 접근하라.
public int getTall(){
return this.tall;
}
public void setDiff(double diff){
this.diff = diff;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}
// 필요한 메소드(함수)를 구현하라.
class Manager {
private static String[] name = {"bob", "john", "alice", "nana", "tom", "sandy"};
private static int[] tall = {172, 183, 168, 161, 171, 172};
private int curIndex;
private Student[] students;
private Manager() {}
private Manager(int length){
this.curIndex = 0;
students = new Student[length];
}
public static Manager makeManager(Scanner in) {
Manager manager = new Manager(Manager.name.length);
System.out.print("input continuously 6 indices(index) of array: ");
// 0 ~ 5 사이의 서로 다른 6개의 숫자(임의의 순서)들을 연속적으로 입력 받으면서
// 학생 객체를 생성한 후 manager에 등록한다.
for(int i = 0; i < Manager.name.length; i++) {
int j = in.nextInt();
// manager 객체의 append 메소드를 실행하여 학생 객체 등록
// append()는 manager내의 학생 객체 배열에 순서적으로 삽입한다.
manager.append(new Student(name[j], tall[j]));
}
return manager;
}
public void displayAll(){
System.out.printf("name\ttall\tdifference\n");
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++){
this.students[i].printStudent();
}
}
public void calculateMean(){
double total = 0;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++){ //total 구하기
total += this.students[i].getTall();
}
total /= this.students.length;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++){ //diff 구하기
this.students[i].setDiff(this.students[i].getTall() - total);
}
System.out.printf("tall mean:%.2f\n\n",total);
this.displayAll();
}
public void append(Student s){
students[curIndex++] = s;
}
public void findStudent(String name){
boolean findFlag = true;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++){
if(students[i].getName().equals(name)){
findFlag = false;
students[i].printStudent();
}
}
if(findFlag){
System.out.println(name+": not found.");
}
}
public void findStudent(String name, int tall) {
boolean findFlag = true;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++){
if(students[i].getName().equals(name) && students[i].getTall()==tall){
findFlag = false;
students[i].printStudent();
}
}
if(findFlag){
System.out.println(name+": not found.");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Manager manager = Manager.makeManager(in);
// manager = new Manager(3);
// 위 문장의 주석을 제거하면 Manager 생성자 접근할 수 없다는 에러가 발생하여야 한다.
while(true) {
System.out.print("\n0.Exit 1.DisplayAll 2.CalculateMean\n");
System.out.print("3.FindStudent 4.FindStudent2 5.MakeManager >> ");
int input = in.nextInt();
if (input == 0)
break;
switch (input) {
case 1: manager.displayAll();
break;
case 2: manager.calculateMean();
break;
case 3: System.out.print("name? ");
String pname = in.next();
manager.findStudent(pname);
break;
case 4: System.out.print("name, tall? ");
pname = in.next();
int tall = in.nextInt();
manager.findStudent(pname, tall);
break;
case 5: manager = Manager.makeManager(in);
break;
}
}
in.close();
}
}
3. 대충 풀이
1) 기존의 main() 함수 내에 있던 String[] name, int[] tall 변수를 Manager 클래스의 static private 멤버로 옮겨라.
이건 너무 쉬우니까 패스...
2) 아래 main() 함수에서 호출하는 Manager.makeManager(in) 문장을 참조하여 Manager 클래스에 해당 함수를 구현하라. 기존 [문제 4-1]의 main 함수에 있던 manager 객체 생성하는 코드들(while 문장 앞까지의 코드)를 makeManager(in) 함수로 옮기면 된다. 그리고 생성된 manager 객체를 리턴하면 된다.
public static Manager makeManager(Scanner in) {
Manager manager = new Manager(Manager.name.length);
System.out.print("input continuously 6 indices(index) of array: ");
// 0 ~ 5 사이의 서로 다른 6개의 숫자(임의의 순서)들을 연속적으로 입력 받으면서
// 학생 객체를 생성한 후 manager에 등록한다.
for(int i = 0; i < Manager.name.length; i++) {
int j = in.nextInt();
// manager 객체의 append 메소드를 실행하여 학생 객체 등록
// append()는 manager내의 학생 객체 배열에 순서적으로 삽입한다.
manager.append(new Student(name[j], tall[j]));
}
return manager;
}
Manager.makeManager로 호출하였으므로 해당 메소드는 static 이어야하므로 static으로 선언해준다.
① Manager 객체를 생성한다.
② 생성된 Manager 객체에 append 메소드를 통해 학생 정보를 넣어서 학생객체 배열을 관리할 수 있도록 해준다.
③ 설정이 끝난 Manager 객체를 반환해준다.
3) Manager 객체는 항상 makeManager(in) 함수를 사용하여 생성하고 사용자가 직접 new Manager(3) 형태로 호출하여 객체를 생성할 수 없게 하라.
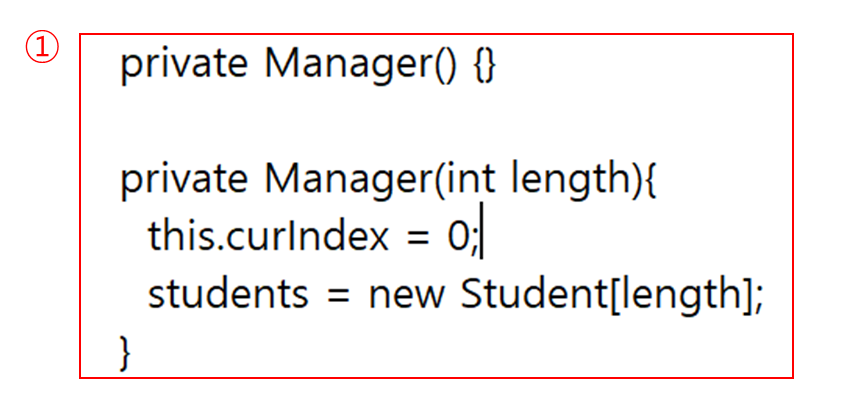
① 사용자가 직접 new 키워드를 사용하여 객체를 생성하지 못하도록 생성자를 private로 선언해준다.
4) 기존 main() 함수를 아래 main() 함수로 교체하라. (너무 쉬우니 패스)
5) 메뉴 항목 "4.FindStudent2"를 선택할 경우 manager.findStudent(pname, tall)가 호출된다.이 함수를 구현하라. 이 함수는 Manager가 관리하는 학생 중에 입력된 이름과 키가 각각 pname과 tall과 동일한 학생을 찾아 출력한다. 찾지 못한 경우 적절한 에러 메시지를 출력한다.
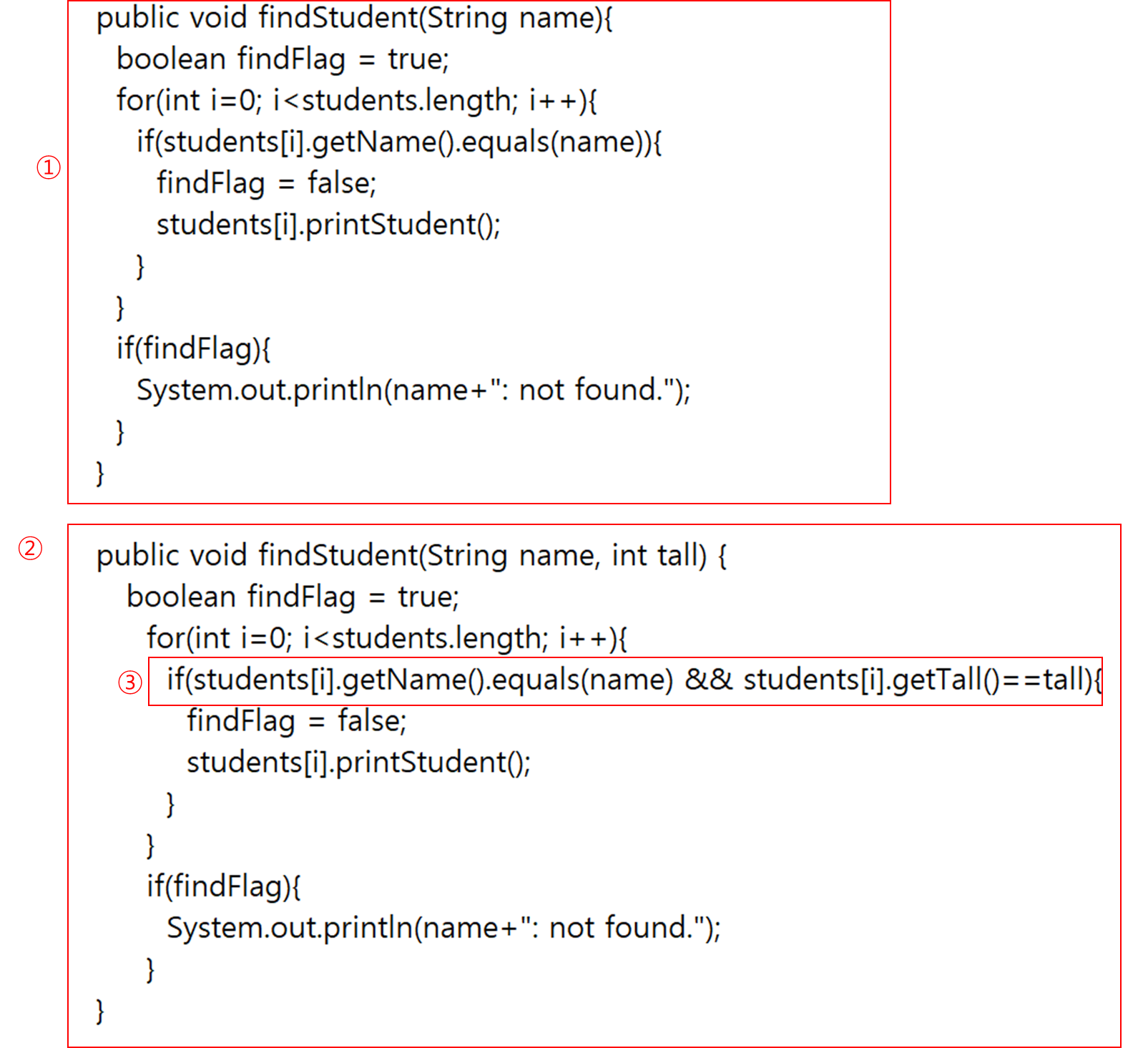
기본적으로 기존 findStudent 메소드와 같다.
① 기존의 findStudent이다.
② 새로 생성된 findStudent이다. Main 메소드를 보면 3번 또는 4번 모두 manager.findStudent를 호출하고 있다. 이는 바로 메소드 오버로딩을 이용하라는 의미이다. (같은 메소드 이름이지만 메소드 시그니처를 다르게 하여 서로 구분하는 것) 매개변수 갯수를 다르게 하여 메소드 오버라이딩을 구현하였다.
③ 새로 생성된 findStudent 로직 중 기존과 다른 점은 그저 키까지 같이 비교하는 부분이다. AND(&&) 조건을 이용하여 구현하면 끝~
'코딩이야기 > 연습문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [라이브코딩 연습] JAVA 실습문제 4-1 (0) | 2022.11.01 |
|---|---|
| JAVA 실습문제 3-2 (0) | 2022.10.28 |
| JAVA 실습문제 3-1 (0) | 2022.10.28 |
| JAVA 실습문제 3-3 (0) | 2022.10.25 |